por
John R. Fischer, Senior Reporter | June 20, 2023
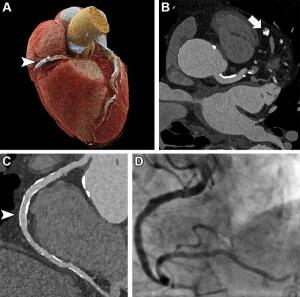
Photon-counting CT may make coronary CT angiography feasible in patients at high risk for coronary artery disease.
Because of its high resolution, photon-counting CT can more accurately estimate calcifications in coronary artery disease to show the true extent of blockages and plaques, reducing false positives and making it feasible in high-risk patients ineligible for coronary CT angiography (CCTA).
CCTA can identify the disease in low- or intermediate-risk patients, but is not recommended for patients at high risk because calcifications tend to “bloom” in its images. When combined with photon-counting CT, the technique is called retrospective ECG-synchronized ultra-high-resolution coronary CT angiography (UHR-CCTA).
In a recent study, UHR-CCTA was highly sensitive and specific in detecting coronary artery disease in 68 patients with severe aortic valve stenosis, with a median overall image quality score of 1.5 on the 5-point Likert scale (one being excellent and five, nondiagnostic). Nearly 80% of its segments were good or excellent.



Ad Statistics
Times Displayed: 123124
Times Visited: 7135 MIT labs, experts in Multi-Vendor component level repair of: MRI Coils, RF amplifiers, Gradient Amplifiers Contrast Media Injectors. System repairs, sub-assembly repairs, component level repairs, refurbish/calibrate. info@mitlabsusa.com/+1 (305) 470-8013
"It is the radiologist's responsibility to determine which protocol is most appropriate for each patient. This flexibility is excellent news for providers, as a broader spectrum of patients can now be assessed noninvasively for cardiac CT, optimizing healthcare resources and potentially patient outcomes," lead author Dr. Muhammad Hagar, from the department of diagnostic and interventional radiology at the University of Freiburg, in Germany, told HCB News.
While not widely available, Hagar expects photon-counting CT to become more accessible over the next decade. While the greater number of emitted photons boost resolution, UHR-CCTA also increases radiation exposure. Hagar says that methods are being developed to reduce this.
While this protocol is not suitable for every patient, he says many can undergo photon-counting CT scanning with other dose-saving protocols, and that the technology can help them avoid ineffective, invasive treatments.
The researchers are studying photon-counting CT’s potential in oncological imaging, as well as for cardiac subgroups not able to undergo CT imaging, such as those with stents, and for heart muscle assessments.
"I think photon-counting CT will be the preferred choice for follow-up imaging after coronary stent implantation to assess vascular patency. This would likely lead to a decrease in diagnostic invasive angiography, which will have a positive impact on reducing both patient risk and, eventually healthcare costs. For this transformative shift to occur, there needs to be a significant reduction in the price of the scanners using photon-counting technology, making it more accessible in a wide range of healthcare settings," he said.
Another recent study found that the modality
had better cardiovascular image quality at a similar dose rate than dual-source CT in infants with suspected heart defects.
The findings were published in
Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).

