Oxipit scores CE marking for ChestEye radiology imaging suite
por
John R. Fischer, Senior Reporter | February 06, 2019
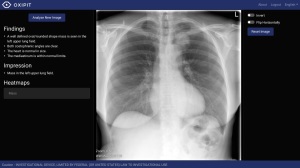
ChestEye radiology imaging suite
AI-based medical imaging provider Oxipit has scored CE marking for its ChestEye radiology imaging suite, designed to provide analysis and preliminary reports on 75 common radiological findings.
The Lithuanian enterprise now has the green light to begin distribution of its solution in 32 European countries where it expects to provide the largest scope of diagnosis available on the market, with an average area under curve metric of 93 percent.
"ChestEye covers the widest scope of pathologies currently available on the market, around 90 percent of diagnoses a hospital or a clinic encounters on a daily basis. We are working to push the coverage even further," Oxipit CEO Gediminas Pekšys told HCB News. "We clearly differentiate ChestEye as a suite solution, which could be easily integrated into the workflow of a radiology department, thereby minimizing the requirements for additional screens and control panels."
Considered by Oxipit to be the first AI-based full workflow medical imaging suite to achieve CE certification, the ChestEye imaging suite relies on a fully automatic CAD platform for detecting findings, localizing features found on a radiograph as a heat map. It also provides a standardized preliminary text report of all relevant radiological information from within a chest X-ray.
Using its Search module, users can compare their findings to ones stored in a given database, with the solution using a neural network to detect similarities based on the present pathology and its location and severity, among other aspects. This allows clinicians to rely on retrospective cases with similar radiological appearances as a basis of their research and work.
In addition, the suite prioritizes patients based on urgency, placing up front unhealthy ones that require urgent specialist attention. This reduces time-to-treatment for those with time-sensitive conditions such as pericardial effusion, pneumothorax, or catheter or intubation malposition.
Evaluated in an internal trial, the solution was found to save 30 percent of time for each patient and reduce errors by up to 50 percent.
Pekšys says further innovations, such as new AI functions, will continue to raise these statistics, and create access to new and essential capabilities.
"We are actively exploring ways to benefit the human user from this difference," he said. "One such case, which is already in our product, is the capability of AI to compare visual features of an image to a database of millions in less than a second. Another case we're testing is if AI assistance can turn the tide in X-ray screening for lung nodules – a use case where current research is uncertain about whether a radiologist alone is effective enough to justify screening."
He adds that the incorporation of HL7 and FHIR protocols will aid in this task. "As more software providers are adopting HL7 and FHIR, or at least including them in their road maps, this addition will help ChestEye to be future-proof and reduce the effort needed to integrate with a large segment of providers worldwide. Strong and widely adopted standards are key to enabling both development and adoption of more advanced AI applications, and should encourage AI companies to set more ambitious goals."
The ChestEye suite supports DICOM protocol and can easily be integrated into the PACS or RIS workflow infrastructure of a radiology department.
It can be deployed on premises or with cloud-based software.
|
|
|
You Must Be Logged In To Post A Comment
|
