por
John R. Fischer, Senior Reporter | June 25, 2018
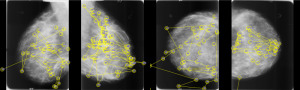
A radiologist's gaze pattern during
examination of a mammogram
Interpretation is in the eye of the radiologist – and with it contextual bias, the presence of which can make all the difference in whether a scan is read accurately or not.
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee are hoping to reduce errors derived from this influence through the development of an AI-powered solution based on their study of the roles played by eye movement and cognitive processes in mammogram interpretation.
“There's a dearth of research on the effect of the subjective nature of visual perception and cognitive judgment, both of which are essential in medical image interpretation. Contextual bias examines whether a radiologist's visual search pattern and diagnostic decision for a specific case may be influenced by the radiologist's judgments for prior cases,” Gina Tourassi, team lead and Director of ORNL's Health Data Sciences Institute, told HCB News. “Our study confirmed that such influence indeed exists, although its magnitude differs across radiologists. This allows us to detect any systemic patterns of visual behavior which correlate with diagnostic error.”



Ad Statistics
Times Displayed: 123124
Times Visited: 7135 MIT labs, experts in Multi-Vendor component level repair of: MRI Coils, RF amplifiers, Gradient Amplifiers Contrast Media Injectors. System repairs, sub-assembly repairs, component level repairs, refurbish/calibrate. info@mitlabsusa.com/+1 (305) 470-8013
As the second leading cause of death in women, early detection of breast cancer is essential and places more pressure on clinicians to accurately diagnose its presence. Misinterpretations enable malignancies to grow and spread, creating greater risks to patient health, including death.
Equipping three board-certified radiologists and seven residents with head-mounted, eye tracking devices, researchers recorded raw gaze data by evaluating the eye movement of each while reading 400 images from 100 studies derived from University of South Florida’s Digital Database for Screening Mammography.
Recordings were also made of clinician diagnostic decisions related to the location of suspicious findings and their characteristics with the BI-RADS lexicon system serving as a basis.
Utilizing a series of statistical calculations and a fractal dimension of each participant’s scan path to differentiate eye movement from one exam to the next, researchers found context bias from previous diagnostic experience played a significant role in the interpretations of each, with trainees the most susceptible to it, and experienced users displaying some degree themselves.
The findings were then assessed by deep learning models trained by the researchers on ORNL’s Titan supercomputer to comprehend large datasets, processing the full data sequence to reveal differentiations in the eye paths of participants.

